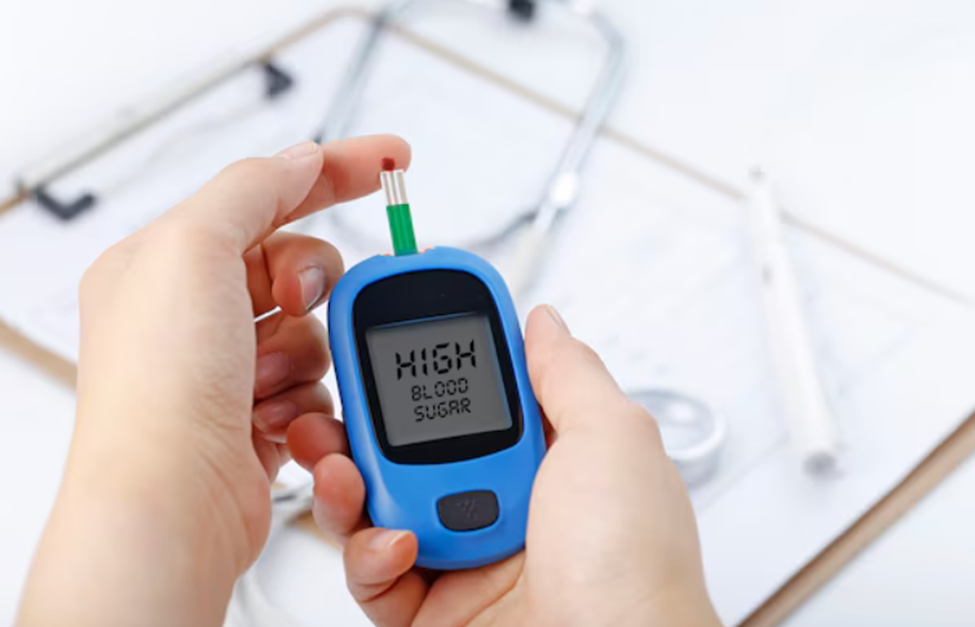
Diabetes (High Blood Sugar Levels): Everything You Need to Know
Diabetes is a chronic health condition. It affects how the body processes blood sugar. Blood sugar, or glucose, provides energy. When diabetes is uncontrolled, blood sugar levels rise. This leads to serious health problems.
Types of Diabetes
Here are the main types of diabetes. Each type has different causes and risk factors.
Primary Types
| Type | Description |
| Type 1 Diabetes | An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The body produces little or no insulin, making daily insulin injections necessary. It usually develops in childhood or early adulthood. Symptoms appear suddenly and require immediate medical attention. |
| Type 2 Diabetes | The most common type is frequently associated with obesity, poor diet, and sedentary lifestyles. The body becomes resistant to insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. It can be treated with lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, insulin. Symptoms appear gradually and can be missed for years. |
| Gestational Diabetes | A minor type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It occurs from hormonal changes that promote insulin resistance. While it normally disappears after childbirth, it raises the mother’s chances of having type 2 diabetes later in life. It calls for dietary adjustments, exercise, and, in some cases, medication. |
Secondary Types
| Prediabetes | A condition in which blood sugar levels are greater than usual but not high enough to warrant a diabetes diagnosis. It serves as a warning indicator of type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, can help to prevent diabetes from progressing to the advanced stage. |
| Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) | A rare, inherited type of diabetes caused by genetic abnormalities that impair insulin synthesis. It typically appears before the age of 25 and is frequently misinterpreted as type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Treatment is based on the genetic mutation and may include medication or insulin therapy. |
| Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA) | Also known as “Type 1.5 Diabetes,” it shares features of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It develops in adulthood and progresses more slowly than type 1 diabetes. It often starts with oral medication but eventually requires insulin therapy. |
| Neonatal Diabetes | A rare form of diabetes that appears within the first six months of life. It is caused by genetic mutations that affect insulin production. Some cases are temporary, while others are permanent. Treatment may include insulin or other specialized medications. |
| Secondary Diabetes | Diabetes that develops due to another medical condition, such as pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, or hormonal disorders. It can also result from prolonged steroid use or other medications. Managing the underlying condition is key to controlling blood sugar levels. |
Symptoms of Diabetes
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes is crucial. Early detection helps prevent complications. Here are the most common symptoms of diabetes:

- Frequent Urination – The kidneys work harder to remove excess sugar.
- Excessive Thirst – Dehydration occurs due to frequent urination.
- Extreme Hunger – The body lacks proper energy conversion.
- Unexplained Weight Loss – The body burns fat for energy instead of glucose.
- Fatigue – Lack of insulin prevents proper energy use.
- Blurred Vision – High blood sugar affects eye health.
- Slow Healing Wounds – Poor circulation slows recovery.
- Tingling or Numbness – Nerve damage results from prolonged high blood sugar.
- Dark Patches on Skin – Insulin resistance causes skin discoloration.
- Frequent Infections – High sugar levels support bacterial growth.
How is Diabetes Harmful?
Diabetes affects multiple organs. If untreated, it causes severe complications. Here is some health risks linked to diabetes:
- Heart Disease – High blood sugar damages blood vessels. This increases the risk of heart attacks.
- Kidney Failure – The kidneys struggle to filter excess sugar. This can lead to kidney damage.
- Nerve Damage – High sugar levels damage nerves. This leads to pain and numbness.
- Vision Loss – Diabetes affects the small blood vessels in the eyes.
- Foot Problems – Poor circulation can lead to ulcers and amputations.
- High Blood Pressure – Diabetes increases the risk of hypertension.
- Dental Issues – High sugar levels increase gum disease risk.
- Skin Conditions – Infections and dryness are common in diabetics.
- Hearing Loss – Nerve damage may affect hearing ability.
- Alzheimer’s Disease – Diabetes is linked to cognitive decline.
Best Possible Solutions for Diabetes
Managing diabetes requires lifestyle changes and medical support. Below are the best solutions for controlling diabetes.
1. Healthy Diet
Eating the right foods helps control blood sugar levels.
- Eat more fiber-rich foods like vegetables and whole grains.
- Avoid processed sugar and high-carb foods.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Reduce intake of saturated fats and fried foods.
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps the body use insulin effectively.
- Walk, jog, or cycle for at least 30 minutes daily.
- Strength training improves muscle glucose absorption.
- Yoga and stretching improve blood circulation.
3. Medication and Insulin Therapy
Doctors prescribe medication based on diabetes type.
- Type 1 diabetics need daily insulin shots.
- Type 2 diabetics may need oral medication.
- Some patients require combination therapy for better control.
4. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight lowers diabetes risk.
- Obesity contributes to insulin resistance.
- Losing even 5-10% of body weight helps improve blood sugar levels.
- A balanced diet and exercise support long-term weight control.
5. Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular blood sugar checks prevent complications.
- Use a glucometer to track sugar levels.
- Maintain a daily record for better management.
- Consult a doctor if sugar levels fluctuate.
6. Stress Management
Chronic stress raises blood sugar levels.
- Practice meditation and deep breathing.
- Engage in hobbies and relaxation techniques.
- Get enough sleep to reduce stress.
7. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking and alcohol worsen diabetes symptoms.
- Nicotine increases insulin resistance.
- Alcohol affects blood sugar control.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake.
8. Routine Medical Check-ups
Regular doctor visits help monitor diabetes progression.
- Get routine blood tests and health screenings.
- Monitor cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
- Follow prescribed treatments and lifestyle changes.
Diabetes is a serious health condition. It affects multiple body functions. Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes is important for early treatment. Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney failure. Managing diabetes requires diet control, exercise, and medication. Regular monitoring and stress management improve quality of life. Follow these solutions to control diabetes effectively. Take action today to prevent complications.
FAQ’s
What is diabetes, and how does it affect the body?
Give detailed view of types of diabetes?
What are the common symptoms of diabetes?
What causes diabetes to develop?
How is diabetes diagnosed?
Can diabetes be cured or reversed?
What are the risks of untreated diabetes?
How can diabetes be managed effectively?
What role does diet play in diabetes management? Is diabetes hereditary or lifestyle-related?