How to Handle Stroke Symptoms and Best Treatment Options
A stroke is a medical emergency that happens when blood supply to the brain is cut off, either by a clot (ischemic stroke) or by a ruptured blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke). Recognizing the symptoms of a stroke and acting early can save lives and limit long-term harm. Here’s how to deal with stroke symptoms and look into treatment options. In this article symptoms of stroke are described with remedies.
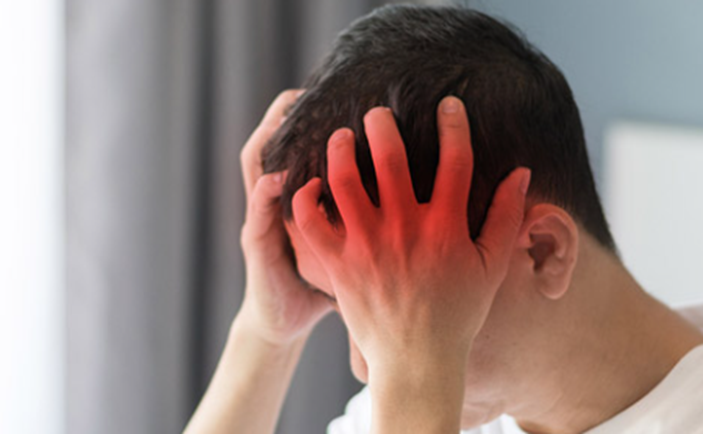

Recognizing Stroke Symptoms
Stroke symptoms often come on suddenly and without warning. Key symptoms to watch for include:
- Sudden Numbness or Weakness: This usually affects one side of the body, particularly the face, arm, or leg.
- Difficulty Speaking: Slurred speech or trouble understanding others is common.
- Vision Problems: You might experience blurred vision or loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Severe Headache: A sudden, intense headache with no known cause could be a sign.
- Dizziness or Loss of Balance: You might feel dizzy, lose your balance, or have trouble walking.
Immediate Action: The F.A.S.T. Method
The F.A.S.T. method is a quick way to check for stroke symptoms:
- F (Face Drooping): Ask the person to smile. Check if one side of the face droops.
- A (Arm Weakness): Ask the person to raise both arms. See if one drifts downward.
- S (Speech Difficulty): Listen for slurred or strange speech. Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence.
- T (Time to Call Emergency service): If each of these symptoms occur, contact emergency assistance instantly. When it comes to treat a stroke, time is essential.
What to Do When a Stroke Occurs
If you suspect someone is having a stroke, act quickly:
- Call Emergency Services: Don’t wait to see if symptoms improve. Call for help immediately.
- Stay Calm: Keep the person calm and comfortable.
- Note the Time: Knowing when symptoms started is crucial for treatment.
- Avoid Giving Food or Drink: Don’t offer anything to eat or drink unless instructed by medical personnel.
Emergency Treatment for Stroke
Once at the hospital, doctors will perform tests to determine the type of stroke. This might include a CT scan or MRI to see what’s happening in the brain. If it’s an ischemic stroke, caused by a clot, doctors may administer a clot-busting drug. This medication works best when used within three hours after the beginning of symptoms. A hemorrhagic stroke, which includes bleeding in the brain, may need surgery or other therapies to halt the bleeding and alleviate pressure.
Recovery After a Stroke
Recovering from a stroke can be a long process and often involves multiple therapies:
- Physical Therapy: Helps regain strength and movement in affected limbs.
- Speech Therapy: Assists in recovering communication skills.
- Occupational Therapy: Helps the individual relearn daily activities.
- Emotional Support: Dealing with the emotional impact of a stroke is also important. Depression and anxiety are common after a stroke, and counseling or support groups may help.
Preventing Future Strokes
After a stroke, taking steps to prevent another one is critical:
- Manage Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is the major cause of strokes. Regular monitoring and treatment can help keep it under control.
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid excess salt, saturated fats, and sugars.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Exercise helps control weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking significantly increases stroke risk. Quitting smoking improves overall health and reduces the risk of future strokes.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive drinking can raise blood pressure and increase stroke risk. Keep alcohol consumption moderate.
Managing Underlying Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of a stroke:
- High Blood Pressure: Work with your doctor to keep it under control.
- Diabetes: Managing blood sugar levels is crucial to reducing stroke risk.
- High Cholesterol: Diet, exercise, and medication can help manage cholesterol levels.
Conclusion
Handling stroke symptoms instantly effectively is crucial to minimizing damage. Identify the symptoms, act quickly, and seek critical medical attention. After a stroke healing and prevention include adjustments to lifestyle, treatments, and possible medication. By adopting these actions, you can increase your chances of survival and lower your risk for future strokes.
FAQ’s
What are the most common symptoms of a stroke?
How can I quickly identify if someone is having a stroke?
What should I do if I suspect someone is having a stroke?
What treatments are available for a stroke? How can I prevent future strokes after having one?