How to Prevent Food Poisoning and Manage Its Effects
Food poisoning poses a major health issue. It happens when you take in infected items such as food or drinks. It’s related to bacteria, viruses, or poisons. Signs might vary from moderate to severe.
Here’s how you can prevent and treat food poisoning effectively.
Practice Good Hygiene
Good hygiene is the first line of defense. It helps prevent contamination.
Wash Your Hands: Always wash your hands before handling food. Use soap and warm water. Wash for at least 20 seconds.
Clean Cooking Surfaces: Disinfect countertops, cutting boards, and utensils. This prevents cross-contamination between foods.
Rinse Fruits and Vegetables: Rinse fresh produce under running water. This removes dirt and bacteria.
Cook Food Properly
Proper cooking kills harmful bacteria. It ensures your food is safe to eat.
Use a Food Thermometer: Check the internal temperature of meats. Poultry should reach 165°F (74°C). Ground beef should reach 160°F (71°C).
Avoid Raw or Undercooked Foods: Raw meals, such as sushi or rare meats, may have bacteria. To prevent risks, cook these meals fully.
Reheat Leftovers Properly: Reheat leftovers to at least 165°F (74°C). This kills any bacteria that may have grown during storage.
Store Food Safely
Proper storage prevents bacterial growth. It keeps your food fresh and safe.
Refrigerate Perishables Promptly: Refrigerate foods like meat, dairy, and eggs within two hours. Bacteria grow rapidly at room temperature.
Use Airtight Containers: Store leftovers in airtight containers. This prevents contamination and keeps food fresh.
Keep the Fridge at the Right Temperature: Set your refrigerator to 40°F (4°C) or below. This slows bacterial growth.
Avoid Cross-Contamination
Cross-contamination spreads bacteria between foods. Preventing it is crucial.
Separate Raw and Cooked Foods: Keep raw meats separate from other foods. Use different cutting boards for meats and vegetables.
Wash Hands After Handling Raw Meat: After handling raw meat, wash your hands immediately. This prevents the spread of bacteria to other foods.
Use Clean Utensils: Always use clean tools to prepare different meals. Do not re-use knives or tongs until first cleaning them.
Be Cautious with Food Preparation
Certain foods require special care during preparation.
Eggs: Cook eggs until the yolks and whites are firm. Avoid foods containing raw eggs, like homemade mayonnaise.
Seafood: Cook seafood thoroughly. Raw or undercooked seafood can harbor dangerous bacteria and parasites.
Dairy Products: Use pasteurized dairy products. Unpasteurized milk and cheese can contain harmful bacteria.
Recognize Symptoms Early
Recognizing food poisoning symptoms early is important. It helps you take action quickly.
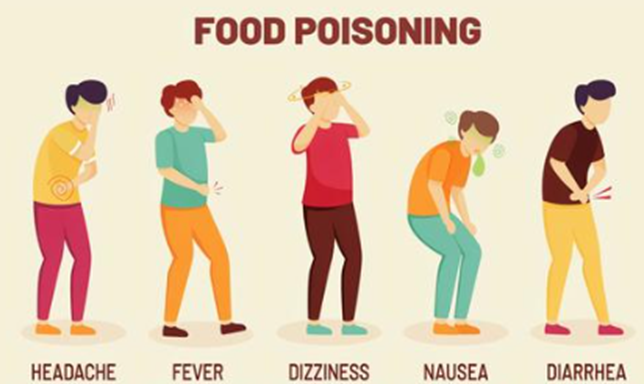
Common Symptoms: The most common signs include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. They might occur for days or hours after consuming food that was contaminated.
Dehydration: Dehydration is a risk with food poisoning. Watch for signs like dry mouth, dizziness, and decreased urination.
Severe Symptoms: Particular signs include high temperature, blood in the feces, and constant vomiting. If you suffer any of the following, get medical treatment quickly.
Treating Food Poisoning at Home
Most cases of food poisoning can be treated at home. Rest and hydration are key.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids. Water, oral rehydration solutions, and clear broths help replace lost fluids.
Rest: Rest allows your body to fight the infection. Avoid strenuous activities until you feel better.
Eat Bland Foods: Once you can eat, start with bland foods. Bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast are gentle on the stomach.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Some cases of food poisoning require medical care.
Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms last more than a few days, see a doctor. You may need antibiotics or other treatments.
High-Risk Individuals: Young children, the elderly, pregnant women, and those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk. They should seek medical care if they suspect food poisoning.
Severe Dehydration: Severe dehydration requires medical treatment. IV fluids may be necessary in some cases.
Preventing Food Poisoning When Eating Out
Eating out poses risks, but you can take precautions.
Choose Reputable Restaurants: Eat at clean, reputable establishments. Check for health inspection scores if available.
Ask About Food Preparation: Don’t hesitate to ask how food is prepared. Avoid raw or undercooked dishes.
Send Back Undercooked Food: If your food is undercooked, send it back. It’s better to be safe than sorry.
Conclusion
Vigilance is required for preventing and treating food poisoning. Maintain excellent hygiene, cook your food correctly, and store it carefully. Avoid cross-contamination and identify symptoms early. Most cases may be managed at home with rest and fluids. Seek medical treatment if your symptoms persist or worsen. Following these procedures will protect you and others from the dangers of food poisoning. Eat safely and with peace of mind.
FAQ’s
What are the most important steps to prevent food poisoning?
How can I tell if food is cooked thoroughly enough to be safe?
What should I do if I suspect I have food poisoning?
How can I prevent cross-contamination in my kitchen?
When should I see a doctor for food poisoning?






