Understanding Pneumonia: Everything You Need to Know
Pneumonia is a serious infection of the lungs. It damages breathing and lungs health. The infection causes the lungs to become inflamed. The air sacs fill with fluid. This is difficult to breathe through. It may be mild or severe. Pneumonia occurs in people of any age. Early treatment is important
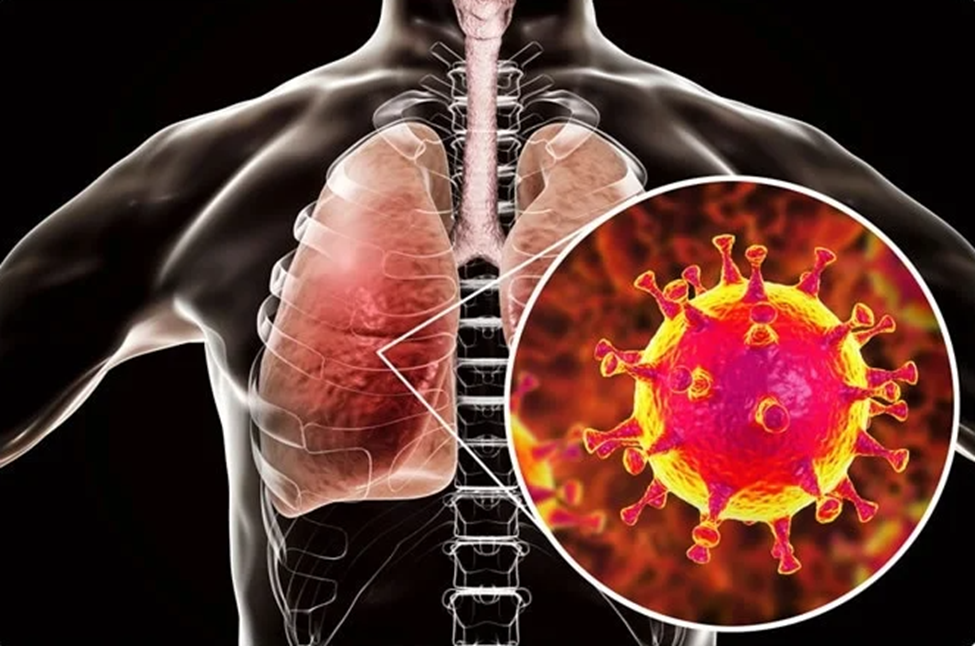
Types of Pneumonia
There are different types of pneumonia. Each has a different cause.
- Bacterial-Pneumonia
Caused by bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Common in adults and older people.
Can develop after a cold or flu.
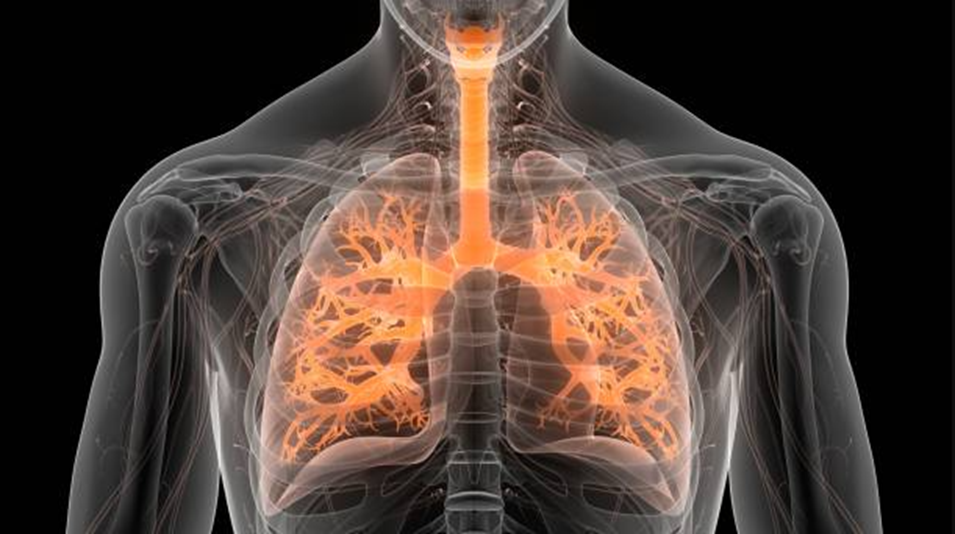
2. Viral-Pneumonia
Caused by viruses like influenza or COVID-19.
More common in children and older adults.
Usually milder than bacterial-pneumonia.
3. Fungal Pneumonia
Caused by fungi found in soil and environment.
Common in people with weak immune systems.
More common in certain regions.

4. Aspiration Pneumonia
Happens when food or liquids enter the lungs.
More common in stroke patients.
Can be serious if not treated.

5. Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia (HAP)
Develops in hospitalized patients.
Often caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
More difficult to treat.
6. Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Develops outside hospitals or healthcare centers.
Caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
Most common type of pneumonia.

Table of all Types of Pneumonia
Part A
| Aspect | Bacterial Pneumonia | Viral Pneumonia | Fungal Pneumonia | Aspiration Pneumonia | Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) | Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) |
| Cause | Bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) | Viruses (Influenza, COVID-19) | Fungi (Histoplasma, Aspergillus) | Inhalation of food, liquid, or vomit | Bacteria in hospitals | Bacteria, viruses, or fungi outside hospitals |
| How It Spreads | Through respiratory droplets | Through airborne viral particles | Inhalation of fungal spores | Not contagious | Contact with contaminated medical equipment | Spread in public places or through air |
| Common Symptoms | High fever, cough with mucus, chills | Cough, fever, fatigue, body aches | Chronic cough, weight loss, fever | Cough with foul-smelling mucus, choking | Severe cough, fever, difficulty breathing | Cough, fever, shortness of breath |
| Severity | Moderate to severe | Mild to moderate | Can become severe in weak immunity | Can lead to serious lung infection | Usually more severe than CAP | Mild to severe, depending on the cause |
Part B
| Risk Factors | Weakened immunity, smoking, age | Infants, elderly, chronic diseases | Weak immune system, HIV/AIDS, cancer | Stroke, dementia, alcohol use | Hospital stays, ventilators, weak immunity | Public exposure, flu season, weak immunity |
| Diagnosis Methods | Chest X-ray, sputum test, blood tests | PCR test, chest X-ray, blood tests | Sputum culture, CT scan, fungal tests | Chest X-ray, swallowing test | Blood tests, sputum culture, X-ray | Blood tests, X-ray, physical exam |
| Treatment | Antibiotics like azithromycin | Antiviral drugs (if needed), rest, fluids | Antifungal medications | Antibiotics, oxygen therapy if needed | Strong antibiotics, ICU care if needed | Antibiotics or antiviral drugs based on cause |
| Recovery Time | 1-3 weeks | 1-2 weeks | Several weeks to months | Depends on severity, can take weeks | Longer recovery, may need hospital stay | 1-3 weeks based on treatment |
| Complications | Sepsis, lung abscess, respiratory failure | Severe breathing issues, secondary infections | Lung scarring, chronic lung disease | Pneumonia, lung infection, breathing problems | Respiratory failure, organ failure | Can worsen into bacterial pneumonia |
| Prevention | Vaccines, hygiene, avoiding sick people | Flu vaccine, hygiene, hand washing | Avoid exposure to fungal spores | Avoid lying down after eating, swallowing therapy | Proper hospital hygiene, monitoring | Vaccination, hygiene, avoiding crowds |
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia has many causes. The main causes include:
- Bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Viruses like influenza or RSV.
- Fungi from the environment.
- Aspiration of food or liquids.
- Weak immune system increases risk.
- Smoking damages the lungs.
- Air pollution worsens lung health.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Symptoms depend on the cause. Common symptoms include:

- Cough with mucus or phlegm.
- Fever and chills.
- Shortness of breath.
- Chest pain while breathing.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Confusion in older adults.
Risk Factors of Pneumonia
Certain people have a higher risk.
- Older adults over 65 years.
- Infants and young children.
- People with chronic diseases.
- Those with weakened immune systems.
- Smokers and alcoholics.
- People exposed to pollution.
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
Not all, but some types of pneumonia are contagious. It’s easy for bacterial and viral pneumonia to spread. Coughs, Sneezes and touching one another are the common ways to spread them. On the other hand, fungal and aspiration pneumonia are not contagious; hard to spread.
Diagnosis of Pneumonia
Doctors use different tests to diagnose pneumonia:
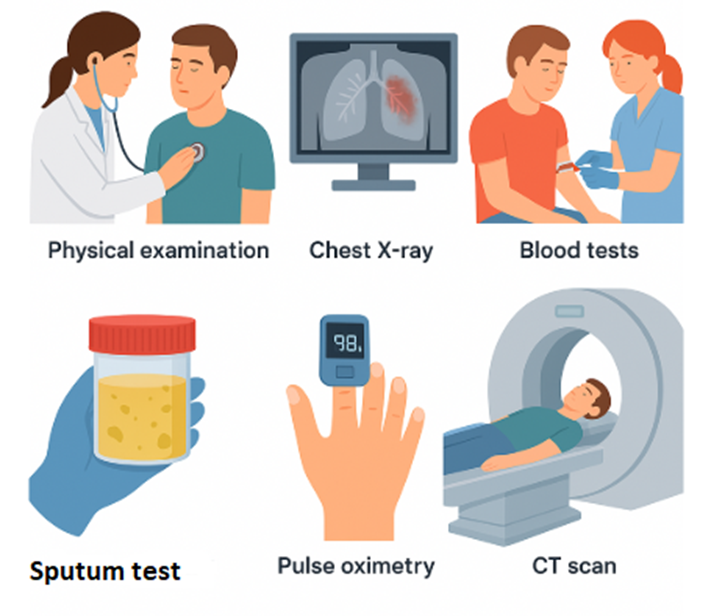
- Physical examination checks breathing sounds.
- Chest X-ray shows lung infection.
- Blood tests check for infection.
- Sputum test finds bacteria in mucus.
- Pulse oximetry measures oxygen levels.
- CT scan gives a detailed lung image.
Treatment of Pneumonia
Treatment depends on the type and severity.
- Bacterial Pneumonia Treatment
- Antibiotics are prescribed.
- Rest and hydration help recovery.
- Viral Pneumonia Treatment
- Antiviral drugs may be given.
- Rest and fluids help symptoms.
- Fungal Pneumonia Treatment
- Antifungal medication is required.
- Treatment takes weeks to months.
- Aspiration Pneumonia Treatment
- Treated with antibiotics.
- Oxygen therapy may be needed.
Home Remedies for Pneumonia

- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Get enough rest.
- Use a humidifier for breathing.
- Take warm soups and herbal teas.
- Gargle with salt water.
- Avoid smoking and pollutants.
Complications of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can cause severe complications.
- Respiratory failure may need ventilator support.
- Sepsis can spread infection in the body.
- Lung abscess forms pus in the lungs.
- Pleural effusion causes fluid around the lungs.
- Organ failure in severe cases.
Prevention of Pneumonia
Prevention is better than cure. Follow these steps:
- Get vaccinated for pneumonia.
- Take flu and COVID-19 vaccines.
- Wash hands regularly.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol.
- Maintain a healthy diet.
- Exercise to strengthen the lungs.
- Avoid polluted areas.
- Treat colds and flu early.
Why Is Pneumonia a Concern in 2025?
Pneumonia remains a leading health issue. Several reasons make it a concern:
- Antibiotic resistance makes bacterial pneumonia harder to treat.
- Air pollution is increasing respiratory infections.
- Climate change affects disease patterns.
- Aging population is more vulnerable.
- New viruses continue to emerge.
- Healthcare costs are rising globally.
- Lack of awareness leads to late diagnosis.
- Weakened immunity due to other diseases.
Future of Pneumonia Treatment
Researchers are working on new treatments.
- Advanced antibiotics for resistant bacteria.
- Better vaccines to prevent pneumonia.
- Artificial intelligence for early diagnosis.
- Telemedicine for faster treatment.
- Personalized medicine for better care.
Pneumonia is a serious condition. Early diagnosis is important. Proper treatment can prevent complications. Preventive measures reduce risks. Global efforts aim to control pneumonia. Staying informed helps in better health management. Always seek medical help if symptoms appear.
FAQ’s
What is pneumonia, and how does it affect the lungs?
What are the main causes of pneumonia?
Main types of pneumonia?
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Is pneumonia contagious, and how does it spread?
How is pneumonia diagnosed by doctors?
What are the best treatments for pneumonia?
What home remedies can help with pneumonia recovery?
Who is at the highest risk for pneumonia?
What complications can arise from untreated pneumonia? How can pneumonia be prevented effectively?